Thirty years back, the mere buying and selling of homes became a commercial industry in Nepal. Individual real estate purchases and sales have been taking place in Nepal for a long time. However, as a corporate industry, this sector has barely been around for around three decades.
Let’s delve deeper into the history of Nepal’s real estate industry.
Rental Properties And Documentation
The very first law in the real estate of Nepal was related to renting property and similar matters. The Department of State Management described this law and Register stated in Muluki Ain section 1853/54. First minister Junga Bahadur Rana approved this law; he also made the land’s documentation be done systematically as the state tariff was the main way to more income for the country. Whether craggy or smooth land, this provision was stated in 1873 and 1874.
Property Income Office
For official land management, the office was built in 1896 called “Maal Adda,”. Likewise Tahasil Karyalaya (The financial institution) was consolidated into it in 1902. The Tahasil was responsible for workers’ pay and collections of bills.
Grouping And Scrutiny Of Land
The country’s land was categorized into four groups: Aval, daum, sehem, and chaar under Chandra Shamsher’s regime, who ruled from 1901 to 1929. The category was for the taxing division on the property, and this was done by a survey in 1907.
Start Of Land Possession
The right of property ownership on official documents began in 1921 when Pota Enrollment Office was built. Also, real estate ownership started passing to Maal Adda in 1922.
Beginning Of A Land Survey
According to the map, the land assessment was established to mark the land and record it in written in Bhaktapur in the year 1923.
Enactment Of The Law
In the 1950s, the first regulation, named The Property Take Over Act, was considered the first law for real estate. Also, the Plot Redress Act was passed to protect and benefit the residents in 1957.
Many laws were approved, such as the Birta Dismiss Bill in 19, the Plot Observe and Quantify Act in 1962, the Lands Act in 1964, and the Land commanding Bill, 1966.
Restructuring The Land Income Office
At first, the Land Management Workplace was set up under the Ministry of Plot Rectify in 9 areas, which had three localities of Kathmandu city, to manage plots and follow the road map as introduced in the Land Observe and Quantify Act in 1962.
The name was changed to the Plot Reform Office in 1967. The Income Office and Fundings and Gathering Offices were also changed into the Land Income Office, initiated in 1969; then the Finance Office looked after it under the Land Income Department.
Past Real Estate Nepal
The boom in Real Estate Nepal started after the 1990s as it brought many businesses related to real estate in Kathmandu and other areas. Many business persons have seen the potential of real estate after legal regulations and laws. Hence, the industry has gone to a new level in Kathmandu and other areas of the country.
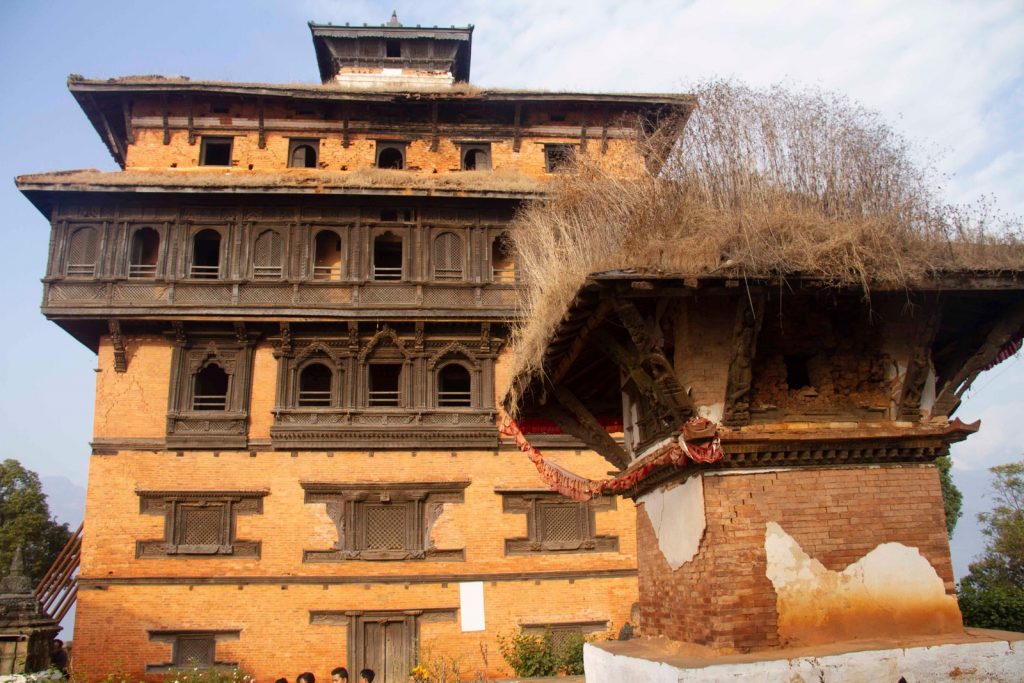

Present Real Estate Nepal
Last 2 decades, we have seen progressing trend in real estates of Nepal. With the emergence of Maoist Insurgency, many people were forced to leave the country. If not, to the urban part of Nepal. This leads to the massive development of real estate in urban part of Nepal. Migrants workers contributions to the economy of Nepal real estate becomes turning point in development of real estate in Nepal. Now, Real estate and housing sector has been ranked as a number one lending sector in Nepalese economy.